48
E
-government, as defined by the
United Nations (2003), refers
to “the use of ICT by government
agencies to improve its internal and
external relations.” More specifically,
it refers to “the use by government
agencies of information technologies
(such as Wide Area Networks, the
Internet, and mobile computing) that
have the ability to transform relations
with citizens, businesses, and other
arms of government.” (World Bank,
2005) The purpose is to use ICT
applications to improve government
administrative efficiency and
effectiveness while strengthening the
government's external responsibilities
towards its citizens, facilitating
and promoting interaction and
communication between government
and the general public.
Howe v e r, w i t h t h e u s e o f
e-government systems on the rise,
establishing a secure and reliable
environment for these systems that
can effectively prevent cybercrimes,
ensure the smooth functioning of
government agency operations,
and protect the rights of citizens,
has become a top priority in the
implementation of e-government.
Since 2007, the TaiwanICDF has
shared Taiwan’s experiences in
the development of e-government
systems with our partner countries
by way of technical cooperation
and helped them expand the scope
of services offered by their own
public agencies. At the same time,
we introduced technologies and
resources from the private sector
in Taiwan to assist our partners in
developing and applying ICT in
different fields. Lately, the TaiwanICDF
has placed more emphasis on
information security management
with the aim of improving partner
countries’ risk management and
adaptive capacities, safeguard
information from threats, and ensure
service continuity of government
agencies.
Introducing international
security standards
in alignment with the
international community
To promote information security
management, the TaiwanICDF
provided on-site support for internal
diagnostics and reviews, information
security management capacity
training, formulation of information
security policies, risk assessment,
implementation of information
security systems, and internal audit,
based on the ISO 27001 information
s e c u r i t y s t a nda r d ( I SO / I EC
27001:2013 – Information Security
Management Systems Certification)
published by the International
Organization for Standardization
(ISO) in 2013. Through this process,
we gradually assisted our partner
countries to establish a common
basis for information security
standard, strengthen the utilization
of information security management
measures, and improve mutual trust
and self-confidence in government
agency operations.
I n 2 0 1 5 , t h e Ta i wa n I CDF
successively helped our partner
countries of Belize, St. Lucia, and
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
to acquire ISO/IEC 27001:2013
information security certification,
becoming the first case of helping
partner countries achieve ISO
certification in Taiwan international
assistance projects.
In the future, these par tner
countries need only reference ISO
international standards and continue
to perform information security
audits and risk reduction processes
to ensure the reliability of their
information security management
measures. The success of these
cooperation projects will also become
the best examples of the TaiwanICDF
concepts of ownership and alignment
with international standards in our
project implementation.
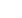
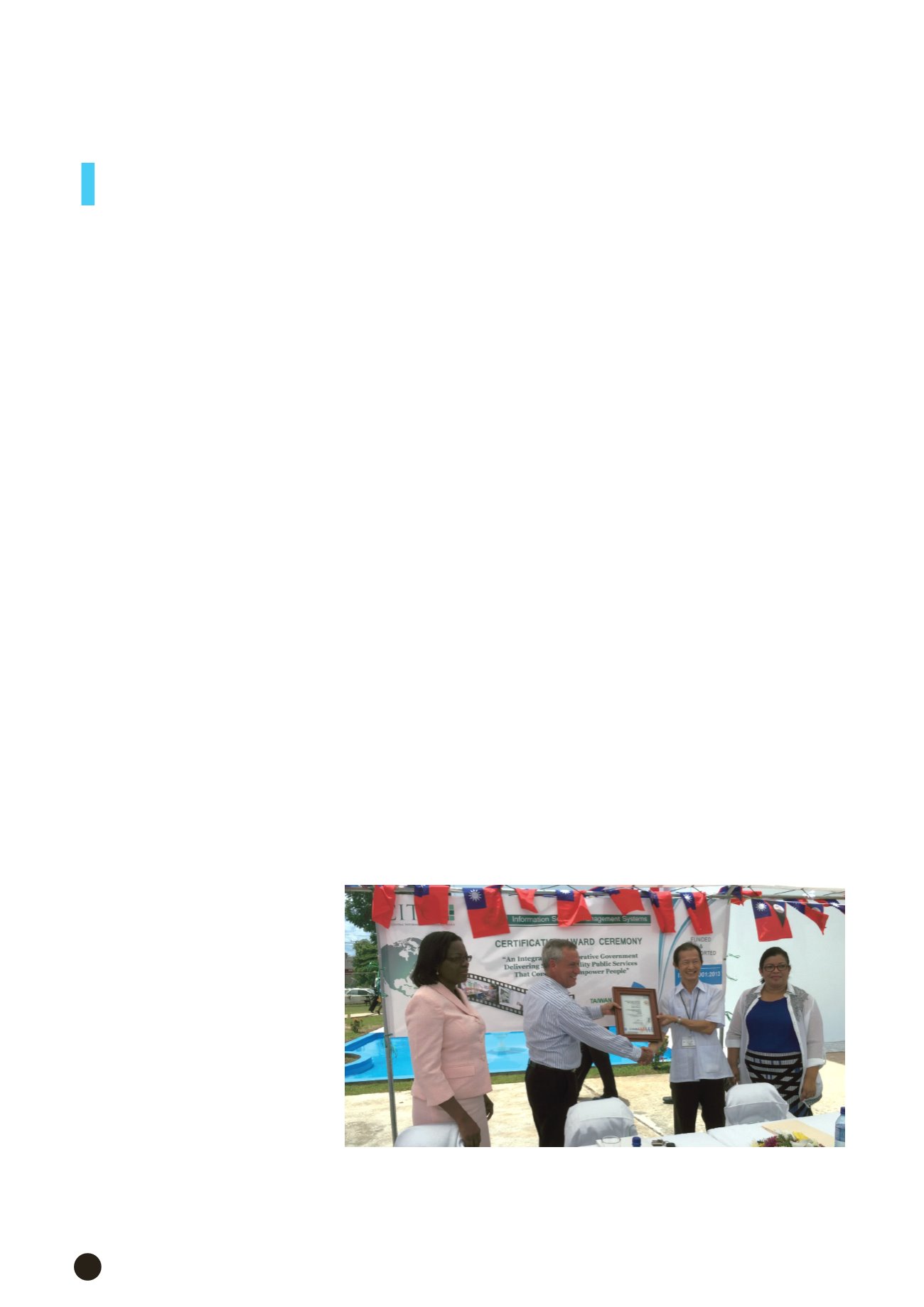
The TaiwanICDF assited the ICT Center of Belize to pass the certification audit for ISO 27001
Information Security Management. Mr. Benjamin Ho (second right), ROC Ambassador to Belize,
hands over the certification to Mr. Joseph Waight (second left), Belize Secretary of Finance.
Change 3
Promoting international information security certification to improve
development of e-government