8
nations in Central America carry out constant monitoring
of the weather and natural environment. This serves as
an important analytical tool for environmental monitoring,
forest conservation, management of land use change,
and disaster prevention and emergency response in these
countries. Furthermore, we have continued to develop
assistance programs relating to renewable energy and
greenhouse gas emission by providing the technical
know-how on natural environmental conservation in order
to assist partner countries to build adaptive capacity to
climate change.
Sharing the responsibility for international
cooperation and development to create a future
of sustainable development together
Despite the remarkable achievements of the MDGs, the
world still faces numerous challenges, including gender
inequality, increasing gaps between the richest and
poorest and rural and urban areas, persistent transnational
conflicts, vast number of people in hunger and poverty,
climate change, and environmental degradation. By
2050, the global population is projected to reach 9
billion and several issues are expected to rise, including
aging populations, continuous urbanization, international
migrant population reaching 232 million, and the need for
education and employment of high youth populations in
developing countries. All of these factors will considerably
worsen the issues of carbon dioxide emission,
deforestation, depletion of ocean resources, and overuse
of water resources, and have become key factors in the
next stages of development assistance work.
To fully resolve the problems that come along with
global development, the United Nations Sustainable
Development Summit approved the 2030 Agenda for
Sustainable Development in September 2015, adopting
the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which
cover environmental, economic and social areas of
development. Overall, 17 goals and 169 targets framed by
the five elements of people, prosperity, planet, justice and
partnership were proposed as foci of development over
the next 15 years (2016-2030).
As the world seeks consensus on important global
development issues, we at the TaiwanICDF hope to
share responsibility in international cooperation and
development. In planning and promoting our operations,
we implement the five principles of the Paris Declaration
on Aid Effectiveness and draw upon our experience
accumulated from working on the MDGs. As well, basing
ourselves on the spirit of the SDGs framework and
referencing the 17 goals and 169 targets, we hold progress
meetings to discuss the organization’s core strategies and
deliberate the future direction of our work, using these as
the context for the next stage of our development work.
Finally, by employing objective and scientific analysis
methods, we will continue to enhance and improve our
organization’s operations.
In terms of strategy, we will continue to practice the
following principles: “respond to international development
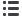
The TaiwanICDF applies remote sensing technologies, geographic
information system, and global positioning system to assist its allies in
Central America in monitoring natural environments. (Photo shows the
Forest Heritage Information Center of the National Institute of Forest
Conservation, Wildlife and Protected Areas (ICF), Honduras.)
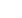
The TaiwanICDF implements healthcare personnel training programs in
our friendly countries to facilitate partner countries’ capacity building in
the fields of public health and medical care. (Photo shows Jessica Clavier,
a student from the St. Kitts and Nevis, receiving clinical training in the
emergency department of the Taipei Veterans General Hospital.)