Strategic Planning and Direction
9
trends, draw on Taiwan’s comparative advantages,
integrate public and private sector resources, and
strengthen cooperative partnerships,” to consider the
best way to increase operational effectiveness and
organizational efficiency, and plan the future overall course
for our medium- and long-term general operations.
In management, we use the “results framework”
approach as our core philosophy. On top of the three
tiers: strategy, development results, and operational
effectiveness and organizational efficiency, we set 36
indicators (see Appendix on p.102) to carry out a full
evaluation on the results of each year’s work plan and
medium-term development plan. This has included adding
many new performance indicators to ensure that each
work item complies with our core strategy, carrying out
project management, improving aid efficiency, staying up-
to-date on foreign aid trends, deepening our knowledge
management goals, and echoing the spirit of the MDGs
and SDGs.
Also, to set the course of foreign aid work toward
sustainable development, we held several work progress
meetings in 2015 to examine each of the key goals and
indicators of the SDGs and the resolutions of the United
Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
During these meetings, we discussed in depth how to
internalize these into our core and regional strategies, as
well as key performance indicators, so that we can share a
common language with our international development aid
partners, fulfill our vision of partnerships for progress and
sustainable development, and together create a future of
sustainable development.
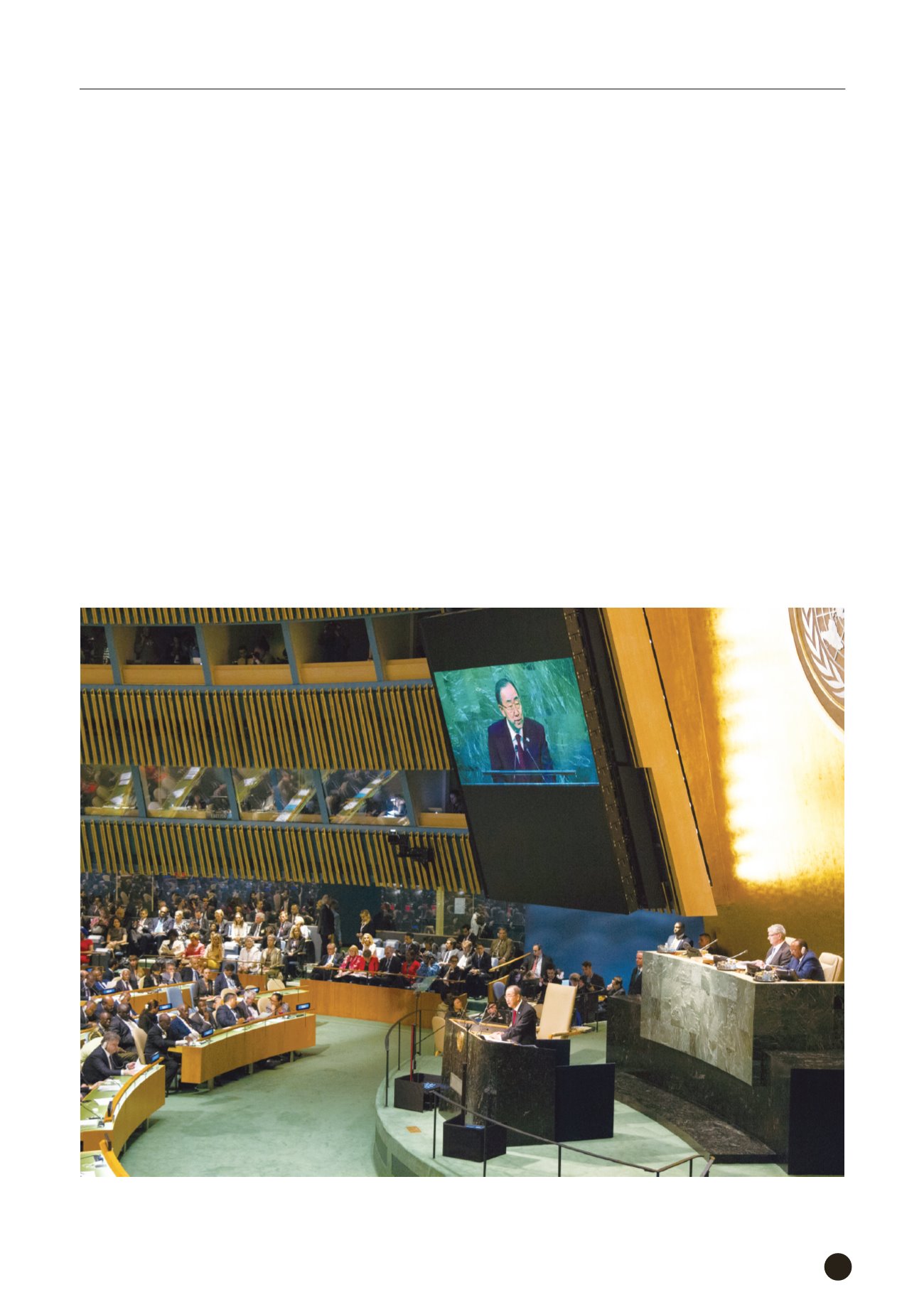
United Nations General Assembly, Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon stands in the center.